The Ins and Outs of Creating a Mobile Cloud Application

-
Ankit Patel
- October 30, 2020
- 4 min read
The vast areas where mobile apps have extended are unlimited. Since the beginning of mobile apps, we have seen them sprawling in almost every industry. They have grown exponentially. Amongst all the innovations in the field, the most recent one is cloud-based applications. Gaining popularity in the data storage industry, these apps have also been found useful in a number of other areas.
● What is a Cloud-Based Mobile App?
A cloud-based mobile app is a software program that has been crafted to be accessed over the digital platform by a number of portable computing devices. Mobile cloud apps are akin to web apps. Both run externally while saving data on a third platform which can be accessed over the net.
However, the truth is not all web apps are cloud apps, which implies that if we wish to run mobile web apps in a virtual environment then they need to be re-engineered. The reason for this is a web app may have initially been written to run and save data on a dedicated physical server present in a certain data center.
A mobile cloud app is a software program that can be accessed from numerous computers and smart devices if they are connected to the internet. By providing access to multiple users, it primarily aims to enhance productivity.
All a cloud-based app needs, to be accessed, is a stable internet connection and a computing device.
● Increasing Popularity of Cloud-Based Mobile Apps:
As per Cisco’s Global Cloud Index, more than 94 percent of workload and computing processes will be performed by cloud data centers by next year.
Even the total revenue garnered by the cloud services market will augment exponentially by the end of this year.
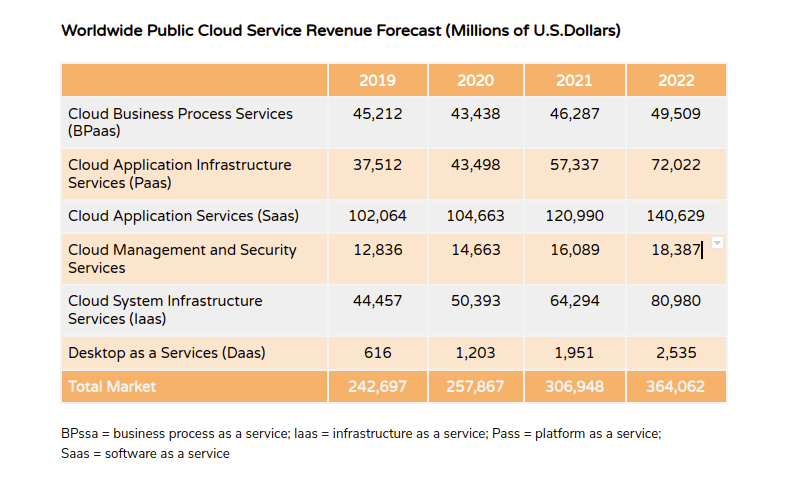
● Cloud Services – Types
There are three main categories in which cloud-based mobile apps can be classified into. The basis of difference is in the architecture of the apps.
- SaaS (Software as a Service)
- IaaS (Infrastructure as a Service)
- PaaS (Platform as a Service)
Let’s look at each of them.
1. SaaS (Software as Service):
The Software as a Service (Saas) is the most evolved type of cloud-based service. Many of the cloud apps this model as it is the largest one. These apps run on third-party hardware located at a remote location.
With SaaS cloud app, users do not have to expend on storing programs on personal hard disks or purchase costly licenses.
2. IaaS, Infrastructure as a Service
With this cloud platform, a third party provides the infrastructure and support in the cloud. The software designer not only creates apps but also offers middleware and in-app support.
Now, you must be wondering what’s middleware?
Middleware is simply an interface between the app and the operating system. It is used to simplify programming and extend extra features to the OS functionality.
With IaaS solutions, developers use an infrastructure similar to that used by Google, Amazon, or Microsoft in their products to regulate the increase in usage.
3. PaaS, Platform as a Service
Needing only the app code from the user’s end, this cloud-based solution, PaaS, stands out from others.
It relieves the users from the need to oversee hardware and operating tasks such as maintenance, procurement. These tasks can easily be outsourced so that developers are completely focused on the app development and support process.
Examples: Google App Engine and OpenShift
– Mobile Cloud apps Versus. Native Apps:
By native app in software development it is implied that an app that is created for a specific platform or device. They have the capability to leverage the latest technology on mobile devices because they are device-specific.
One of the shortcomings faced by developers while drafting a code for a native app is that they need to create a number of versions of the same app if they wish to run on several operating systems.
As cloud apps are accessed from a server and not downloaded on the device, developers have the liberty to write a single code, which can be accessed through any device having a net connection.
– Mobile Cloud Apps versus Web-based Apps:
The major similarity between mobile-based cloud apps and web-based apps is that they both run on external servers and not on the mobile device on which or through which they are accessed. They both save data externally and are used with a browser through the internet.
Nevertheless, a web-based app does not always possess the security features offered by a cloud-based app. There are no major differences between mobile cloud apps and web-based apps in terms of how they perform on a device.
Thus, it can be stated that all mobile cloud apps are web apps but not all web apps can be regarded as mobile cloud apps.
● Struggles Faced When Creating Mobile Cloud Application
All those parties or businesses thinking to create a cloud-based solution can take two routes.
- Become a cloud provider: If you decide to program your own cloud solution, then issues like hardware, security, and data processing logic are to be faced.
- Develop a program that runs on a third-party cloud solution: If you choose this solution then you will have to take care of integration, scalability, and selecting the right cloud service provider.
Following are some of the major challenges faced by developers when creating a mobile cloud app.
- Security
- Ability to Exchange Information with Other Systems
- Performance
One of the major challenges faced by developers while crafting a cloud-based solution is -SECURITY. This is the way it appears in their mind- BOLD CAPITAL LETTERS. Although a number of policies and protocols shield the user authentication and access, security always remains at the crux of the matter.
It is important for a cloud-based app to be able to run on different devices and integrate with other cloud services. As cloud systems do not communicate fully with each other, developers don’t get an opportunity to blend elements from various cloud services.
The app performance and customer experience will certainly be impacted by the number of servers is not large. To achieve optimal conversion rates, the custom UI must be able to load within 3 seconds. If it doesn’t then the additional second taken to load the app will result in a loss of traffic and doubles the bounce rate.
You may also like

How to Choose the Right Mobile App Development Company
-
Ankit Patel
Imagine this: you’ve got a brilliant app idea that could revolutionize your business, take it to new heights, and transform your entire customer experience. But without the right team to… Read More
How Much Does it Cost to Build a Salon Booking App like Fresha?
-
Ankit Patel
We all have witnessed the buzz in the world of beauty & wellness, and it’s booming every day thanks to the fast-paced and stressful lifestyle. In an era where time… Read More
A Complete Guide to Hotel Booking App Development With Cost
-
Ankit Patel
Whether it’s a corporate business trip or a relaxing vacation with friends, finding the right hotel at the right time and a seamless hotel booking experience is not a luxury… Read More